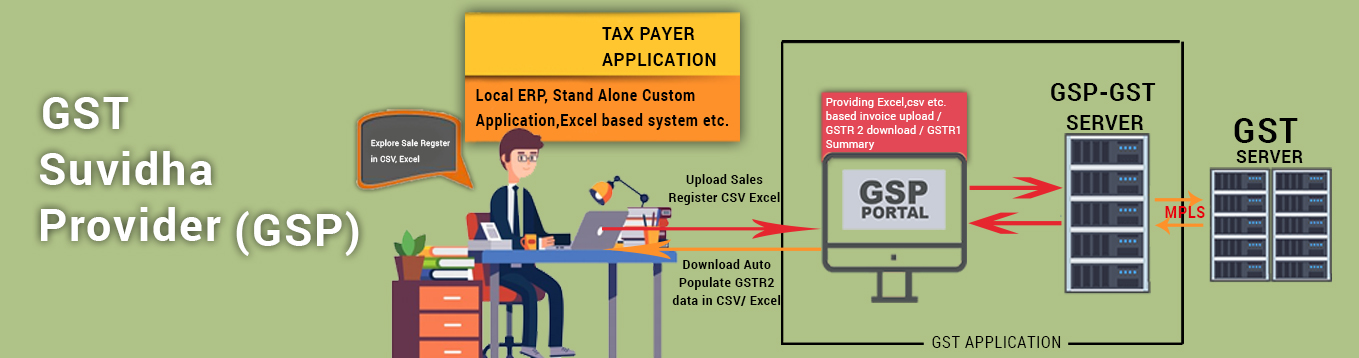
aSujaGST is a partner with NSDL are here to provide e-Gov is a GST Suvidha Provider (GSP) appointed by GSTN for implementing GST across the country. We are also going to provide e-Gov which also offers Application Service Provider (ASP) services to the users. NSDL ASP services can be availed by Dealers, CAs/Tax Consultants and Facilitation Centers to help them with interacting with the GST Systems from uploading of invoices details to the filing of returns and reconciliation. Other ASPs and entities that already have a GST return filing solution can use NSDL e-Gov GSP services to connect to GSTN.






Goods and Services Tax Network (GSTN) has been formed by Government of India under section 25 of Companies Act, 1956, which will host IT infrastructure, systems and provide services to the Central and State Governments, taxpayers and other stakeholders for supporting implementation and administration of GST.
GSTN has given allowance to taxpayers to interface with GST System via aSujaGST applications through secure GST system APIs. aSujaGST developing such applications are called GST Suvidha Provider (GSP). GSP will need to connect to the GST system directly through an MPLS or VPN connection.
The GSPs are contemplated to provide innovative and convenient methods to taxpayers and other stakeholders in interacting with the GST Systems from registration of entity to uploading of invoice details to filing of returns.Thus there will be two sets of interactions, one between the App user and the GSP and the second between the GSP and the GST System.
GSTN believes by creating and balancing an ecosystem of Service Providers viz GST Suvidha Provider (GSP like aSujaGST) providing innovative solutions (Portal, Mobile App, Enriched API) by themselves for making tax filing more easy and convenient to taxpayers
Taxpayer via his choice of aSujaGST applications, which will provide all user interfaces and convenience via desktop, mobile, other interfaces, that will make a return very easy and time-saving and will be able to interact with the GST system. Our applications will connect with GST system via secure GST system APIs
Apart from uploading of invoices & filing of returns, following other services are expected to form GSPs
India introduced GST from 1st July 2017. GST is implemented through Acts and Rules as discussed below:
Acts
Rules
Further, the Government has issued various Notifications, Circulars and Orders for clarifying ambiguity around the GST provisions.
The aforesaid legislations (i.e. Act, Rules, Notification, Circulars and Orders) issued till 8th October are summarized below:
| Legislation | Sections | Schedules to Act | GST Rules | Notifications Rate | Notifications Others | Circulars | Orders |
| CGST | 174 | 3 | 162 | 47 | 66 | 19 | 10 |
| UTGST | 26 | - | Refer CGST Rules | 47 | 17 | - | 1 |
| IGST | 25 | - | Refer CGST Rules | 50 | 12 | 2 | - |
| Cess | 14 | 1 | Refer CGST Rules | 7 | 1 | - | 1 |
| SGST (May vary State to State) | 174 | 3 | 162 | May vary State to State | |||
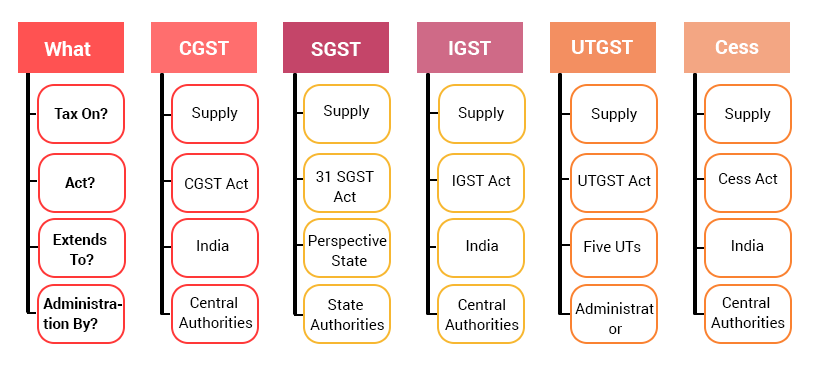
The CGST Act and IGST Act extend to the whole of India. SGST Acts extends to specific State like Maharashtra Goods and Services Tax Act, 2017 extends to Maharashtra State. Further, UTGST Act extends to the Union territories of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, Lakshadweep, Dadra and Nagar Haveli, Daman and Diu and Chandigarh. Compensation Cess Act extends to the whole of India.
It is admissible to note that GST, as well as Cess, is leviable on a supply.
CGST, IGST and Cess Act are administered by Central Authorities. UTGST Act is administered by Administrator. SGST Act is administered by respective State Authorities.
Central Government has introduced CGST Rules (162 to be precise!). Meanwhile, the State Government has issued SGST Rules and these Rules are a replica of CGST Rules. Afterwards, section 20 of IGST Act and section 21 of UTGST Act states that rules made under CGST Act shall mutatis mutandis, apply for IGST/ UTGST.
Section 1 of CGST Act states that the section of the Act shall come into force on such date as the Central Government may, by notification in the Official Gazette, appoint. Similar provision incorporated in IGST, UTGST, Cess Acts. From 1st July 2017, all sections are effective except section 51 and 52 (which deal with Tax Deduction at Source and Tax Collection at Source).
| Effective from | CGST | IGST | UTGST | Cess |
| 22nd June 2017 | Sec. 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 10, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30, 139, 146 and 164 [Not. No. 1/2017-CT] | Sec. 1, 2, 3, 14, 20 and 22 [Not. No. 1/2017-IT] | Sec. 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 17, 21 and section 22 [Not. No. 1/2017-UT] | |
| 1st July 2017 | Sec. 6 to 9, 11 to 21, 31 to 41, 42 , 43 , 44 to 50, 53 to 138, 140 to 145, 147 to 163, 165 to 174 [Not. No. 9/2017-CT] | Sec. 4 to 13, 16 to 19, 21, 23 to 25 [Not. No. 3/2017-IT] | Sec. 6 to 16, 18 to 20 and 23 to 26 [Not. No. 3/2017-UT] | All provisions [Not. No. 1/2017-GSTC] |
| Not yet effective | Sec. 51 (TDS) and 52 (TCS) | |||
Except the proviso to sub-section (9) of section 42
Except the proviso to sub-section (9) of section 43
Supply goods is liable for GST under six tax bracket i.e. 0.25%, 3%, 5%, 12%, 18% and 28%. Further, few goods like aerated drinks, luxury cars, cigar, cigarettes etc attract Cess. Similarly, certain goods is liable for GST under four tax categories i.e. 5%, 12%, 18% and 28%. Further, few services attract Cess.
Multi-tax rates structure certainly makes it necessary for the taxpayer to first determine the categorization of goods or services and then pay GST at the applicable rate.
| Scehdule | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
| CGST and SGST/ UTGST rate | 2.50% + 2.50% | 6% + 6% | 9% + 9% | 14% + 14% | 1.50% + 1.50% | 0.125% + 0.125% |
| IGST Rate | 5% | 12% | 18% | 28% | 3% | 0.25% |
| Scehdule | Rate I (Lower rate) | Rate II (Concessional rate) | Rate III (Standard rate) | Rate IV (Luxury rate) |
| CGST and SGST/ UTGST rate | 2.50% + 2.50% | 6% + 6% | 9% + 9% | 14% + 14% |
| IGST Rate | 5% | 12% | 18% | 28% |
Composition Scheme rate
The Composition scheme that is available to the small business which can pay GST at a lower fixed rate without assailment of ITC which is covered in the tax bracket of 1%, 2% and 5%.
Composition scheme can be opted by the taxpayer when their turnover is less than INR 75 lacs and 50 lacs in particular States. Hereafter, it is increased up to INR 1 Crore by way of Notification 46/2017- CT dated 13th October 2017 by It is pertinent to note that Composition scheme is not applicable to Ice cream and other edible ice, whether or not containing cocoa, Pan Masala and all tobacco goods (As per Not. No. 8/2017-CT and 2/2017-UT).
| Scehdule | Traders | Manufactureres | Dhaba/ restaurant |
| CGST and SGST/ UTGST rate | 0.50% + 0.50% | 1% + 1% | 2.50% + 2.50% |
| IGST Rate | 1% | 2% | 5% |
| Sr. No. | Particulars |
| 1 | Obtain registration if turnover exceeds the prescribed threshold |
| 2 | Determine whether transaction qualifies as supply (including deemed supply). If yes, determine value of the supply. |
| 3 | Determine appropriate Harmonised System of Nomenclature (HSN) or Service Accounting Code (SAC) applicable for the supply. HSN (four digits) are for goods and SAC are for services. |
| 4 | Determine rate of GST (and cess, if applicable) thereon. GST, being indirect tax, can be charged and collected from customer except in case of Composition Scheme dealers. |
| 5 | Issue an invoice for every taxable supply (including deemed supply) made or Bill of Supply for an exempt activity. Invoice, Bill of Supply etc should contain the prescribed particulars. Invoice may not be issued as tax invoice if the value of the goods or services or both supplied is less than INR 200 (subject to fulfilment of prescribed conditions. |
| 6 | Issue an invoice for every taxable supply received which is liable for GST under Reverse Charge Mechanism (RCM). Alternatively, consolidated invoice can be issued |
| 7 | Issue a payment voucher invoice for every taxable supply received which is liable for GST under Reverse Charge Mechanism (RCM). |
| 8 | Avail eligible input tax credit in accordance with Input Tax Provisions |
| 9 | Deposit GST within prescribed time limit. |
| 10 | File applicable GST returns (such as GSTR-1, GSTR-2, GSTR-3, GSTR-3B etc) within prescribed time limit. |
| 11 | Obtain Letter of Undertaking in case taxpayers intends to export goods without payment of IGST (for export). |
| 12 | Display GST registration number on the name / sign board and also Certificate in his business premises. |
Applicability of CRM
Typically, the GST liability is to be dispersed by the supplier of goods/ service or both. However, in particular cases, the liability to pay tax is cast on the recipient of the supply instead of the distributor. This is known as Reverse Charge Mechanism (RCM).
RCM will increase the compliance burden for the recipient as invoice and payment voucher is required to be issued by the recipient [as per section 31 (3) (f) and (g) of CGST Act].
The exemption under RCMVide Not. No. 8/2017-CT an exemption is provided for intra-State supply, under CGST for an aggregate value of supplies of goods or service or both received by a registered person from any or all the suppliers, who are or are not registered, exceeds Rs 5,000/- in a day.
Relaxation of RCM Applicable under section 9(4) of the CGST Act. Reverse Charge Mechanism as applicable to procurement from URD dealer under section 9(4) of the CGST Act are suspended from 13th October 2017 to 31st March 2018.
Compliance under RCMThe taxpayer is required to comply with various CGST rules related to Tax Invoices and Payment Voucher for inwards supplies which attract RCM As per subclause (f) and (g) of section 31 the CGST Act, a registered person who is liable pay GST under RCM shall issue:
Consolidated invoice is important to note that, as per rule 46 of the CGST Rules a registered person may issue a consolidated tax invoice at the end of a month for supplies procured from un-registered person and if the aggregate value of such supplies exceeds rupees five thousand in a day from any or all the suppliers on which the Company is liable to pay GST under RCM.
Further, it is to be noted that as section 9(3) of the CGST Act, RCM is applicable for specified services notified by Not. No. 13/2017- CGST. In case of procurement of said goods and services (Like GTA, Legal Services etc.) separate invoice for each vendor could be required to raised by the taxpayer.
Payment vouchers addition to aforesaid, a payment voucher is also required if the payment is made to vendor covered under RCM. The taxpayer could face many challenges while compliance with said provisions because said provisions are also applicable to the RCM paid for an unregistered person. There could be numerous vendor to whom payments are made by cash or bank and it is one of the challenges to comply with the issue of tax invoice along with payment voucher.
In GST Regime, twelve returns are prescribed. Typically, GSTR-1, GSTR-2 and GSTR-3 will be applicable for most of the taxpayers, there are specific returns such as GSTR-4 for composition dealers, GSTR-5 for non-resident etc.
| Return Form | Particulars | Applicability |
| GSTR-1 | Details of outward supplies of taxable goods and/or services effected |
|
| GSTR-2 | Details of inward supplies of taxable goods and/or services effected claiming input tax credit | |
| GSTR-3 | Monthly return on the basis of finalization of details of outward supplies and inward supplies along with the payment of amount of tax | |
| GSTR-4 | Return for Composition taxable person | Every registered person paying tax under Composition scheme (Section 10 of the CGST Act) is required to file GSTR -4 |
| GSTR-5 | Return for Non-Resident foreign taxable person | Every registered non-resident taxable person shall furnish a return in FORM GSTR-5 electronically through the common portal, either directly or through a Facilitation Centre notified by the Commissioner. |
| GSTR-6 | Return for Input Service Distributor | Every Input Service Distributor shall require to furnish return in GSTR-6 |
| GSTR-7 | Return for authorities deducting tax at source (TDS) | This form is applicable to every registered person required to deduct tax at source under section 51 of the CGST/SGST Act. Kindly note that TDS provisions are yet to be made effective. |
| GSTR-8 | Details of supplies effected through e-commerce operator and the amount of tax collected (TCS) | This form is applicable to every electronic commerce operator required to collect tax at source under section 52 the CGST/SGST Act. Kindly note that TCS provisions are yet to be made effective. |
| GSTR-9 | Annual Return |
|
| GSTR-10 | Final Return | Every registered person whose registration has been cancelled shall furnish a final return within three months of the date of cancellation |
| GSTR-11 | Details of inward supplies to be furnished by a person having UIN and claiming refund | Every person who has been issued a Unique Identity Number and claims refund of the taxes paid on his inward supplies. |
| GSTR-3B | Summary return | This is summary return to be filed for till March 2017. |
The periodicity of GST returns and the due dates are given as under:
Relaxation during initial period of GST Implementation
GST council has extended the due date of filing of monthly returns ie. GSTR-1, GSTR -2, GSTR-3 etc. for the initial period. In this regard, the due dates for the returns are as below:
| Return Type | Notification No. | Remark | ||||||||||||||||||||
| GSTR-1 | Notification No. 57/2017-CT |
The periodicity for GSTR-1 is Quarterly for the persons who is having turnover up to 1.5 crores. Due dates is as follows.
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Notification No. 58/2017-CT |
Extension of the due dates for GSTR-1 for monthly periodicity. The revised Due dates are as follows
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| GSTR-5 | Notification No. 60/2017-CT | With respect to GSTR-5 applicable to Non-resident taxable person the due dates for the month of July,2017, August, 2017, September, 2017 and October, 2017 extended to 11th day of December, 2017. | ||||||||||||||||||||
| GSTR-5A | Notification No. 61/2017-CT | GSTR-5A applicable to person supplying OIADA services from a place outside to person supplying online information and database access or retrieval services from a place outside India to a non-taxable online recipient referred to in section 14 of the Integrated Goods and Services Tax Act, 2017 the due dates for the month of July,2017, August, 2017, September, 2017 and October, 2017 extended to the 15th day of December, 2017. | ||||||||||||||||||||
| GSTR-6 | Notification No. 62/2017-CT | The due dates of the GSTR-6 which is required to be filed by an Input Service Distributor for the month of July is extended up to 31st December, 2017. Further, for the month of August, 2017, September, 2017 and October, 2017 shall be subsequently notified in the Official Gazette | ||||||||||||||||||||
| GSTR-4 | Notification No. 63/2017-CT | Extension of GST ITC 04 required to be filed quarterly by the principle with respect to goods send to Job work extended from 30thNovember,2017 to 31st December,2017. |
GSTR-3B
Further, a chanages has been made applicable up to December 2017, to taxpayers who are required to file GSTR-1, 2 and 3. GSTR-3B is a summary return and containing details of outward and inward supplies alongwith other details. In this regard, the due dates are as given below:
| GSTR-3B | Due date |
| July 2017 |
|
| August 2017 | 20th September 2017 |
| September 2017 | 20th October 2017 |
| October 2017 | 20th November 2017 |
| November 2017 | 20th December 2017 |
| December 2017 | 20th January 2018 |
| January,2018 | 20th Feb,2018 |
| February,2018 | 20th March,2018 |
| March,2018 | 20th April ,2018 |
The entire process if GSTR-1 (Outward Supply Return), GSTR-2 (Inward Supply Return) and GSTR-3 (Monthly return) is online and it is expected that GSTR-2 of purchaser will be auto-populated based on the GTSR-1 filed by the suppliers. The chart below gives a broad outline of the process:
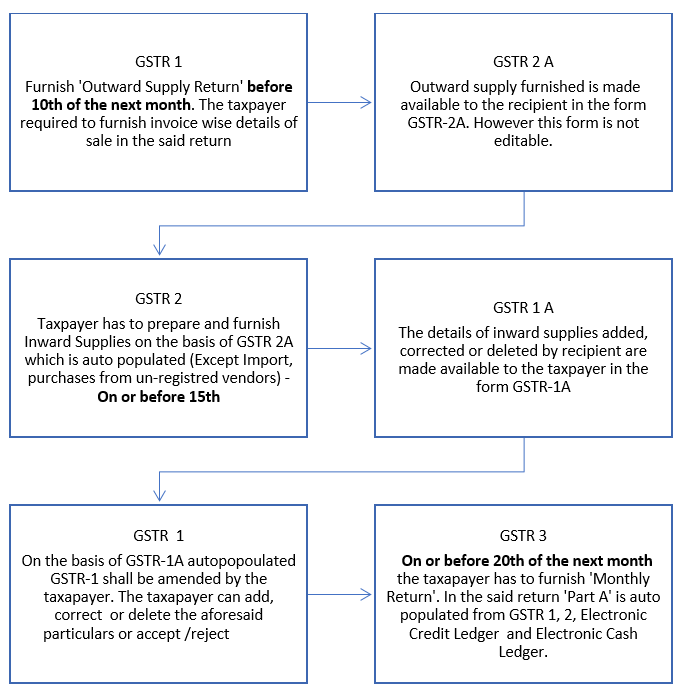
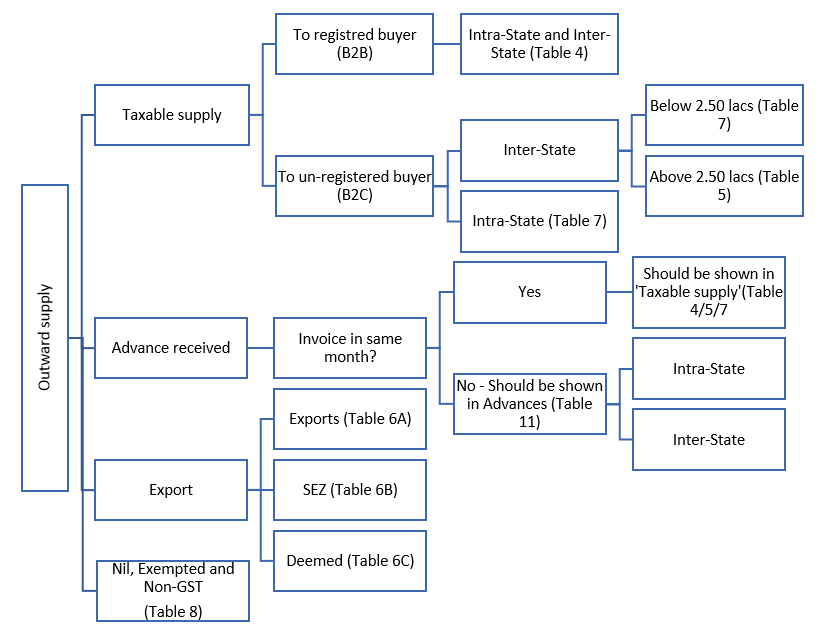
GSTR-1 is an Outward Supply Return in which taxpayer is required to furnish invoice-wise, consolidated and other details as discussed below:
Invoice wise details of:
Consolidated details of:
Other Details
Further, this return is required to be furnished on or before 10th of the next month
The chart given below provide the overview of details required to be provided in this return.
GSTR-2 is an Inward Supply Return in which taxpayer is required to furnish invoice-wise, consolidated and other details as discussed below:
Invoice wise details of:
Consolidated details of:
Other details:
Further, this return is required to be furnished from 11th to 15th day of the next month.
The chart given below provide the overview of details required to be provided in this return.
GSTR-3 is required to be furnished on or before 20th day of the next month. This return consists of two parts, Part A and Part B. Details required to be filled in Part A of the return is auto populated from GSTR-1 and GSTR-2 whereas Part-B is required to fill by the taxpayer.
Further, Part-B of the return contain the details of electronic cash ledger and electronic credit ledger from which taxpayer is required to discharge his liability towards tax, interest, penalty, fees or any other amount payable under the Act or the provisions of this chapter by debiting said ledger.
The chart given below provide the overview of details required to be provided in this return.
GSTR-3B is required to be furnished on or before 20th day of the next month. This is the summary return and applicable up to December 2017. This return mainly covered details with respect to
Outward Supply
Inward Supply
Hereinunder, the taxpayer has to provide the details of input tax credit availed, ineligible input tax credit, reversal of input tax credit if any. Further, the taxpayer has to bifurcate the procurement details in to:-
Seamless flow of ITC is a primary objective of GST. Hence, acoording to section 16 (1) registered taxable person, subject to fulfilment of prescribed conditions is entitled to take credit of input tax charged on any supply of goods or services or both to him which are used or intended to be used in the course or furtherance of his business.
Overview of the provisions and rules
Section 16 and 17 of CGST Act deals with eligibility and restriction for availment of ITC by a register person. Section 18 of the Act related to availability of ITC in special circumstance like allowability of ITC where a register person ceases to pay tax under composition scheme and opt normal scheme. Further, CGST Rules for Input Tax Credit (relevant Rules being 36 to 45) are also notified through Not. No. 7/2017-CT. These rules mainly prescribes the conditions for availment of ITC, reversal of ITC in certain scenario, computation of reversal etc.
| Term | Definition |
| Input - Section 2 (59) | means any goods other than capital goods used or intended to be used by a supplier in the course or furtherance of business |
| Input service - Section 2 (60) | means any service used or intended to be used by a supplier in the course or furtherance of business |
| Capital goods - Section 2 (19) | means goods, the value of which is capitalised in the books of accounts of the person claiming the credit and which are used or intended to be used In the course or furtherance of business |
It is pertinent to note that the aforesaid definitions are very wide and can cover under its ambit any input, input service or capital goods provided it is used or intended to be used by the supplier in the course or furtherance of business (unless specifically excluded under section 17).
ITC will now be available provided the credit is appearing in the Electronic Credit Ledger online! Thus, unlike current service tax and excise law, the credit will be effectively dependent on the vendors as unless vendors file the appropriate returns, GST credit will not be available to the recipient.
Further, Section 16 (2) of the Act, prescribes these conditions for availment of credit:
Therefore said , inter-alia, two conditions appears to be un-justified as typically, among those first condition is,putting such a kind of onerous condition on buyer leads to un-necessary burden and may pave way of litigation. Credit should be available on the basis invoice and recipient should not be burdened with the responsibility of knowing whether the tax has actually been credited to the Government or not.
Section 16 (2) (b) of the CGST Act prescribes that for availment of input tax credit, inter-alia, services should be received. The condition of receipt of goods can be proved through GRN (Goods Received Note) however, it services are intangible in nature and thus its not clear why a condition of receipt of service is provided for.
Further, as per Rule 36 of CGST Rules, the input tax credit can be availed only by a registered person, including the Input Service Distributor, on the basis of any of the following documents, namely which proves that its the user
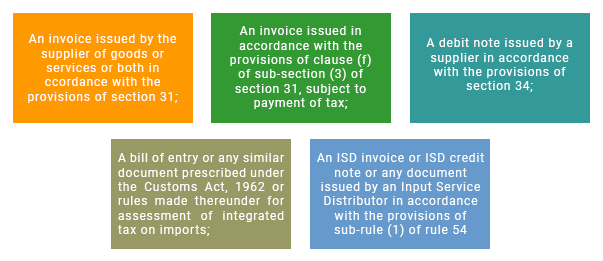
Input tax credit will be availed by a registered person only if all applicable particulars as prescribed in CGST Rules are contained in the said document, and the relevant information, as contained in the said document, is furnished in FORM GSTR-2 by such person.
Input tax credit will be availed by a registered person only if all applicable particulars as prescribed in CGST Rules are contained in the said document, and the relevant information, as contained in the said document, is furnished in FORM GSTR-2 by such person.
Utilisation of ITC
Intra-State supply of goods and services attract CGST and SGST whereas inter-State supply of goods and service attract IGST. Further, the utilisation of CGST credit for the payment of SGST and visa-versa is not allowed under the Act. The table given below depict the manner of utilisation of ITC
| Credit of | Utilisation |
| IGST | First against IGST then against CGST and later against SGST |
| CGST | First against CGST then against IGST |
| SGST | First against SGST then against IGST |
Section 17 (5) provides that input tax credit will not be available on following:
It was expected that in GST regime, seamless credit will be allowed to business houses without any delima or any restrictions except say goods / services which are availed for personal use than official use (something similar to Unite Kingdom VAT law).
However, surprisingly, inter-alia, aforesaid credit would continue to be not available (in respect of both goods or services). Further, credit is denied on goods and/or services used for personal consumption. Also, input tax credit shall not be available on goods lost, stolen, destroyed, written off or disposed of by way of gift or free samples. This continuation of denial will lead to substantial tax cascading (as rate of GST will be higher than the current rate of service tax!).
Credit will be available on those product like rent-a-cab, life insurance and health insurance only if the Government notifies these services as obligatory for an employer to provide to its employees under any law. Also, creditwill be provide on food and beverages, outdoor catering, beauty treatment, health services, cosmetic and plastic surgery will be available. All this is available if used as inward supply for making an outward taxable supply of the same category or as an element of a taxable composite or mixed supply.
Also, another round of litigation as interpretation issues will crop up while determining eligibility or otherwise of GST paid on personal consumptions such as business lunch with clients.
A person who is registered shall have authority to avail ITC charged on any supply of goods or services or both which are used or intended to be used in the course or furtherance of his business. However, proportionate reversal of ITC could be trigger in the scenario given here under:
Given that afterwards,the credit to the extent of use for taxable or business supplies will be available. The Rule also provides for segregation of credit, at invoice level itself.Rule 42 of Input Tax Credit Rules, prescribes for apportionment of credit on inputs and input services and Rule 43 of the Input Tax Credit rule prescribe methodology for apportionment of ITC with respect to Capital goods.
Finally, on actual basis for the financial year, reversal should be done, before the due date for filing the return for the month of September following the end of the financial year to which such credit relates. Hence, interest will be payable if finally it is determined that the credit availed was more. Herein, short availment will not entitle taxpayer to claim credit from Government!
Reversal of ITC if payment to vendor has not made within 180 Days To continue to claim the input tax credit the buyer has to ensure that he pays the supplier within 180 days from date of invoice. If payment to vendor is not made within 180 days, then proportionate input tax credit will have to be reversed in FORM GSTR-2 for the month immediately following the period of one hundred and eighty days from the date of issue of invoice (refer Rule 37 of CGST Rules). In this regard, please note the key provisions as given below:
Let us discuss some key provisions related to availment and utilisation of ITC.
Time limit for availment of ITC
A registered person shall not be allowed to take input tax credit in respect of any invoice or debit note for supply of goods or services or both even after the due date of furnishing of the return under section 39 for the month of September following the end of financial year to which such invoice or invoice relating to such debit note pertains or furnishing of relevant annual return, whichever is earlier.
Double benefit of GST is not allowed
In case where registered person has claimed depreciation on the tax component of the cost of capital goods and plant and machinery under the provisions of the Income-tax Act, 1961, the input tax credit on the said tax component shall not be allowed.
Time of availment of ITC in case of installment
It is provided that where the goods against an invoice are received in lots or instalments, the registered person shall be entitled to take credit upon receipt of the last lot or instalment. To claim credit, taxpayer will have to track now whether the goods are received in one lot or multiple.
As per section 15 of CGST Act, GST is payable on the transaction value. Transaction value is the price actually paid or payable for the said supply of goods and/or services if:-
Section 15 (2) precisely provides for inclusion and exclusion from value as discussed below:
| Include | Exclude |
| Any taxes, duties, cesses, fees and charges levied under any law for the time being in force other than GST Act. | The value of the supply shall not include any discount before or at the time of the supply if such discount has been duly recorded in the invoice issued |
| Any amount that the supplier is liable to pay in relation to such supply but incurred by the recipient of the supply and not included in the price actually paid or payable. | The value of the supply shall not include any discount after the supply has been effected if such discount is in terms of agreement and Doccument issued by the supplier |
| Incidental expenses, including commission and packing, charged by the supplier to the recipient | |
| Interest or late fee or penalty for delayed payment of any consideration for any supply | |
| Subsidies directly linked to the price excluding subsidies provided by theCentral Government and State Governments |
Other Aspect of valuation
As per section 15 (4) of CGST Act empowers the Government to make Rules. Further, section 20 of IGST Act and section 21 of UTGST Act states that rules made under CGST Act shall mutatis mutandis, apply for IGST/ UTGST. Valuation related Rules comprises of 8 Rules from Rule 27 to Rule 35 of CGST Rules.
Reference to the valuation rules is necessary to be taken where transaction value as defined under section 15 of the CGST Act is not acceptable. Therefore, transaction value will not be acceptable if:
In the after mentioned scenario reference of valuation rules are required to be taken for determination of value to levy GST. The table given below shows the valuation provisions:-
| Particulars | Rule | Applicable to | Open Market Value | Like kind and quality (LKQ) | 90% of price charged to 3rd party LKQ | 110% Value | Rule 30 or 31 (residual) |
| Supply to distinct or related person1 | 282 | Goods or services or both | Yes | Yes | Yes3 | Yes | Yes |
1This Rule will typically cover inter-State Stock / branch transfers
2Value determined cannot be challenged by Authorities if recipient is eligible for full input tax credit
3This valuation (90%) is an option available to supplier and where the goods are intended for further supply to third party customers by recipient
| Particulars | Rule | Applicable to | Open Market Value | Like kind and quality (LKQ) | 90% of price charged to 3rd party LKQ | 110% Value | Rule 30 or 31 (residual) |
| Agent | 29 | Goods | Yes | - | Yes4 | - | Yes |
| Exchange | 27 | Goods or services | Yes5 | Yes | - | - | Yes |
| Cost basis | 30 | Goods or services or both | - | - | - | Yes | - |
| Residual | 316 | Goods or services or both | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
4This valuation (90%) is an option available to supplier and where the goods are intended for further supply to third party customers by agent
5If OMV is not available then total value of money and money equivalent
6Service provider has option to choose Rule 5 disregarding Rule 4
Rule 27 of the CGST Rules helps in determination of value of goods or services where the consideration is not wholly in money. In such case the value would be either:
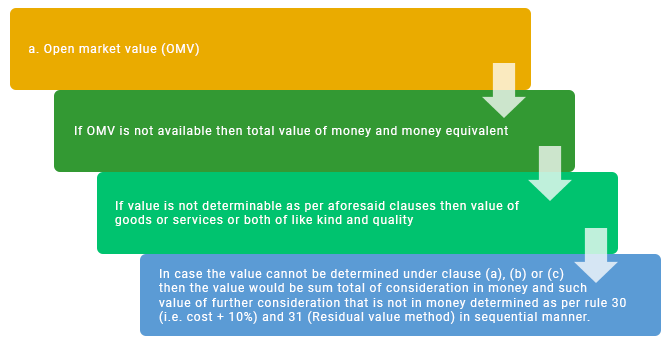
As per information given (at the end of the Rules), OMV is termed as to mean open market value of a supply of goods or services or both means the full value in money, leaving out the integrated tax, central tax, State tax, Union territory tax and the cess payable by a person in a transaction, where the supplier and the recipient of the supply are not related and the price is one and only consideration, to obtain such supply at the same time when the supply being valued is made.
There could be the possibility to arise many issues like how to determine value if multiple open market values are available and thus determining open market value would pose practical challenges. Similarly, determining value of services of like kind and quality could be practically difficult.
Illustrations provided in Rule 27 of CGST Rules are reproduced below:
It may be noted that no illustration for valuing services provided on say barter basis is provided in the aforesaid Rule.
The Rule splits the transaction in two broad baskets as under.
a. Where recipient is eligible for full input tax credit
Value declared in invoice shall be deemed to be the open market value of goods or services. This is a big relief as the valuation will not be questioned by the Authorities where the credit is fully available. Certainly, this provision will ease out valuation pains of many sectors such as banks, telecom, insurance etc.
b. b. Where recipient is not eligible for full input tax credit
Rule 29 helps in determination of value of supply of goods made or received through agent. Typically, in such case the value would be:-
Determining open market value would pose practical challenges. Further, though the Rule provides for alternate valuation mechanism i.e. 90% of value could be difficult as the value (at which agent will sell to end customer) will not be available at the time of supply of goods by principle to agent.
Illustration provided in Rule 29 of CGST Rules are reproduced below:
A principal supplies peanut to his agent and the agent is supplying peanut of like kind and quality in subsequent supplies at a price of five thousand rupees per quintal on the day of the supply. Another independent supplier is supplying peanut of like kind and quality to the said agent at the price of four thousand five hundred and fifty rupees per quintal. The value of the supply made by the principal shall be four thousand five hundred and fifty rupees per quintal or where he exercises the option, the value shall be 90 per cent. of five thousand rupees i.e., four thousand five hundred rupees per quintal.
Rule 30 applies if value cannot be obtainable as per any of the preceding Rules. As per this Rule the value will be
Application of this Rule has two hurdles:
Reasonable means Consistent with general principle
Where the value of supply of goods or services or both cannot be determined under rules 27 to 30, the same shall be determined using reasonable means consistent with the principles and the general provisions of section 15 and the provisions of this Chapter. This Rules provides an option to supplier of services to opt for this Rule than Rule 30 (as determination of cost of provision of services could be challenging).
Option l
Option ll
Value will be deemed as:
Travel Agent - Rule 32 (3)
This sub-rule prescribes methodology to determine value in case of sale of air tickets by travel agent. The value in such cases will be:
Explanation - For the purposes of this sub-rule, the expression "basic fare" means that part of the air fare on which commission is normally paid to the air travel agent by the airlines.
Value in case of insurance - Rule 32(4)
The value in such cases will be:
t is also provided in the Rule that nothing contained in this sub-rule shall apply where the entire premium paid by the policy holder is only towards the risk cover in life insurance.
Value in case of second hand goods - Rule 32(5)
Value will be difference between selling and purchase price (and where the value of such supply is negative it shall be ignored) provided there is no change in nature of goods and credit on purchased second hand goods is not availed by dealer. In case the value determined is negative, i.e. goods are sold at loss then GST will not be payable.
Also, vide Not. No. 10/2017-CT an exemption from CGST is provided for intra-State supplies of second hand goods received by a registered person, dealing in buying and selling of second hand goods and who pays the central tax on the value of outward supply of such second hand goods as determined under sub-rule (5) of rule 32 of the Central Goods and Services tax Rules, 2017, from any supplier, who is not registered, from the whole of the central tax leviable thereon under sub-section (4) of section 9 of the Central Good and Services Tax Act, 2017 (12 of 2017).
1. Compulsory Registration
2. Voluntary Registration
Compulsory Registration
As per section 22 of the CGST Act, every supplier shall be liable to get themselves registered under CGST Act in the State or Union territory, other than special category States, from where he makes a taxable supply of goods or services or both, if his aggregate turnover in a financial year goes beyond twenty lakh Rupees.
It is also stated that where such person makes taxable supplies of goods or services or both from any of the special category states, he shall be liable to be registered if his aggregate turnover in a financial year goes over ten lakh rupees.
Voluntary Registration
A person who intent to obtain registration under GST however aggregate turnover of that person in a financial year does not exceed the specified limit (i.e. ten or twenty lakh rupees) may obtain voluntary registration under GST. Also, all provisions of this Act, as are applicable to a registered person, shall apply to such person.
Where aggregate turnover is defined under section 2(6) of the CGST Act as given hereunder aggregate turnover means the aggregate value of all taxable supplies (excluding the value of inward supplies on which tax is payable by a person on reverse charge basis), exempt supplies, exports of goods or services or both and inter-State supplies of persons having the same Permanent Account Number, to be computed on all India basis but excludes central tax, State tax, Union territory tax, integrated tax and cess;
Given the aforesaid key aspects taken in to consideration while computing aggregate turnover for the purpose of GST are:-
Include
Exclude
As per section 23 of the CGST Act, following persons are not liable for to register under GST:-
1. Any person engaged exclusively in the business of supplying goods or services or both that are not liable to tax or wholly exempt from tax under this Act or under the Integrated Goods and Services Tax Act
2. An agriculturist, to the extent of supply of produce out of cultivation of land.
Among, all other person if engaged in any supply of goods and services are liable to register compulsory wheather aggregate turnover in a financial year exceeds twenty lakhs and ten lakhs in specified state.
Further, as per sub clause 2 of Section 23 of the CGST Act, the Government may, on the recommendations of the Council, by notification, specify the category of persons who may be exempted from obtaining registration under this Act.
Certain categories of the persons are liable for compulsory registration even the aggregate turnover is not more than twenty lakh as or ten lakh for specified state. In this regard, as per section 24 of the CGST Act, the persons given below are required to register compulsory even aggregate turnover does not exceed the specified limit.
Further the Government on the recommendations of the Council may be notified such other person or class of persons that are required to apply for compulsory registration.
As discussed aforesaid as per section 24 of the CGST Act, the persons making any inter-State taxable supply is liable to register under GST irrespective of aggregate turnover as specified for compulsory registration. However, as per notification 10/2017 - Integrated Tax specifies that the person making inter-State supplies of taxable services and having an aggregate turnover, to be computed on all India basis, not exceeding an amount of twenty lakh rupees in a financial year is exempted from obtaining registration. Hence, no compulsory registration for the unregistered dealer engaged in interstate supplies and having aggregate turnover up to Rs. 20 lacs or Rs.10 lacs in case of special category states.
Every person, intent to obtain registration other than the person as specified is required to follow the procedure as given hereunder

Other Key aspect of registration
Following are some of the key aspect which should be taken in to consideration while registration
As a GST Suvidha Provider, NSDL e-Gov will be providing the entire gamut of GSP as well as Application Services Provider (ASP) services which would include but not limited to:

This service will allow the customer to generate invoices in printable format.

This offline utility will validate, convert invoices into GSTN format and also directly upload invoices to NSDLgst ASP.

This service will allow the customer to upload sales invoices as well as file GSTR 1 return.

This service will allow the customer to download counterparty sales invoices from GST portal for matching purposes.

This service will allow the customer to upload final GSTR-2 return after matching of purchases with those downloaded from GST portal..

This service will allow the customer to download/view cash and credit ledgers from GST Portal.
This service will allow the customer to submit cash/ credit utilization towards GST payable
This service will allow the customer file GSTR 3 return.
Matching invoices as per dealer & as per GSTN.